Rabat – Once upon a time, there was a Roman city called Volubilis in what was known as the Kingdom of Mauritania, which encompassed parts of modern Morocco and Algeria. The Romans chose the city as their municipium in North Africa around 44 AD; it played a significant role in Rome’s political, economic, and cultural presence in the region.
The city was no different from other Roman cities; Roman citizenship was also granted to elites and soldiers of the native Amazighs, since it was a municipality rather than a colony.
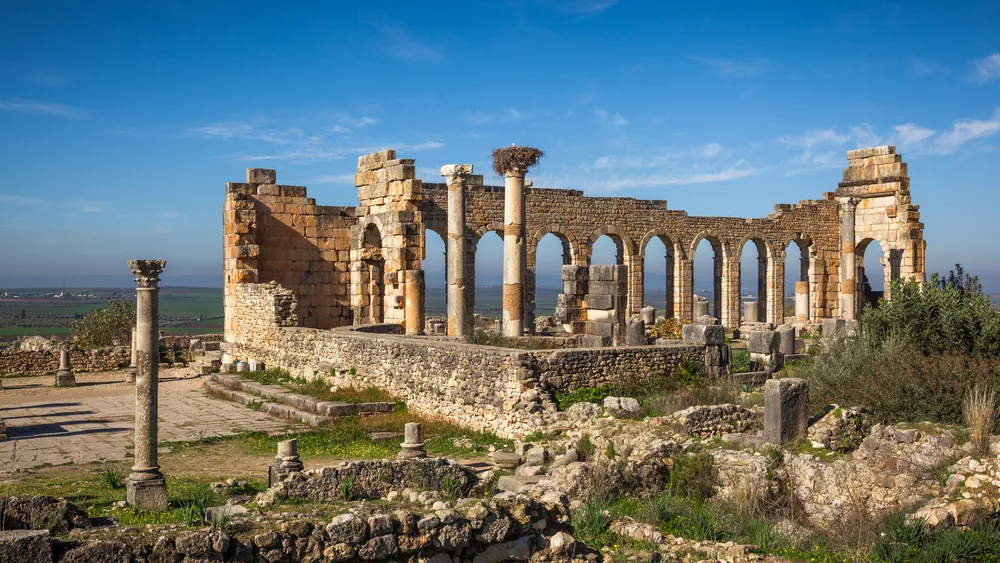
Volubilis is a mystical Moroccan city situated in the vast region of the Saïss, a region mostly famous because it is where the iconic city of Fez is located.
The city of Volubilis was discovered only recently, and some of it is still buried underground due to sedimentation, decay, and other natural factors. Although the locals were aware of the ruins, it wasn’t formally studied as an archaeological site until the 1910s, when French archaeologists Louis Chatelain and Henri Terrasse began their work.
Louis Chatelain is known as the first archaeologist to conduct major excavation work on the site, while Henri Terrasse added to Chatelain’s work by putting the excavated monuments into the Moroccan historical context, dating back to the Roman era when parts of Morocco were under Roman control.
The city once had a prestigious Roman-style triumphal arch, basilicas, buildings with stunning mosaics, and more. Volubilis was no different from a regular Roman city.
Volubilis: the ghost of a city affected by the greed of its people
The Romans eventually withdrew from the area around 285 AD. The Roman Empire was known for its military force, technological advancements, and innovations – especially in architecture. The Romans were therefore a dominant force for centuries, but they were also known for their corrupt leaders.
Historians often relate the decay of the Roman Empire to the greed of those who ruled in its later years. The greed for power and wealth of Roman emperors, magistrates, and senators contributed to the spread of poverty and inequality within the Roman Empire, which in turn played a role in its eventual demise.
Volubilis is one of the cities that attests to the presence of what was once the largest empire in the world in North Africa, specifically in Morocco.